
V. A. Kornienko, N. F. Blagoveshchenskaya, and T. D. Borisova
Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, St. Petersburg, Russia
B. Thidé
Swedish Institute of Space Physics, Uppsala Division, Uppsala, Sweden
A. Brekke
Auroral Observatory, University of Tromsö, Tromsö, Norway
It is known that heating of the D and E region electrons by amplitude-modulated powerful high frequency (HF) radio wave pumping of the ionosphere gives rise to a corresponding modulation of the ionospheric conductivities and therefore to current disturbances in a localized region of the lower ionosphere. Changes of ionospheric conductivities and currents are produced by electron temperature disturbances as well as electron density changes. Changes of the electron temperature is more efficient at low altitudes and for short time intervals while the electron density changes are more important at somewhat higher altitudes and for longer time intervals. Modification of the D and E region ionosphere at ULF frequencies can be used to artificially generate a magnetic response of up to 10 nT [Stubbe, 1996, and references therein]. ULF waves within the Pc3-4 range observed from HF pumping experiments in the F2 region were reported by Blagoveshchenskaya et al. [1992, 1995, 1998a], Blagoveshchenskaya and Troshichev [1996], Belenov et al. [1997], and Yeoman et al. [1997]. It should be noted that during these experiments a continuous HF pumping rather than amplitude-modulated pumping was used. Belenov et al. [1997] and Yeoman et al. [1997] attributed the observed ULF waves to naturally occurring geophysical phenomena. Results obtained by Blagoveshchenskaya et al. [1998a] clearly demonstrate that there exists a relation between the HF pump power level and the magnitude of the Doppler frequency shift oscillations, appearing in the signals scattered from artificial field-aligned irregularities (AFAI). This confirms the hypothesis of an artificial origin of the observed ULF waves within the Pc3-4 range caused by powerful HF radio waves. However, the explanation for possible generation mechanisms of the ionospheric and magnetic pulsations observed during HF pumping experiments is still an open question, particularly for long-period pulsations of large amplitudes. Recent results of ULF wave activity observed in an ionospheric HF pumping experiment performed in the nocturnal auroral ionosphere at Tromsö were presented by Blagoveshchenskaya et al. [1998b].
Here we report in detail on coordinated observations of ionospheric and magnetic pulsations within the range 100-120 s observed in an experiment on 17 February 1996 at the Tromsö heating facility (geographical coordinates 69.6oN, 19.2oE, L=6.2, magnetic dip angle I=78o ) during an auroral substorm in the premidnight hours. The unique features of the experiment are as follows: (1) The powerful HF radio wave interacted with an auroral sporadic Es layer. Therefore the upper hybrid region was close to altitudes of the HF pump-enhanced conductivity level and the auroral electrojet. (2) Continuous rather than an amplitude-modulated HF pumping of the ionosphere was used. This means that the period of the pulsations observed was shorter than the duration of the pumping cycle.
Ionospheric pulsations excited by the powerful HF wave were studied with the use of the field-aligned scattering method of diagnostic HF radio waves. The observations of HF diagnostic signals scattered from artificial field-aligned irregularities (AFAI) were made by Doppler equipment. The magnetic variation data from Tromsö were obtained at the Tromsö University Auroral Observatory. Data from the Tromsö dynasonde, the IMAGE magnetometer network [Viljanen and Häkkinen, 1997], IMP 8, and LANL spacecrafts were also used in the analysis of our experimental results.

|
| Figure 1 |
|
| Figure 2 |
The heating facility at Tromsö was operated at the frequency 4040 kHz, O mode polarization with heating cycles 4 min on/6 min off beginning at 2000 UT. The HF pumping was directed nearly along the geomagnetic field by tilting the antenna beam 6o to the south. The HF effective radiated power (ERP) was about 150 MW.
Doppler measurements of HF diagnostic signals were carried out on the London-Tromsö-St. Petersburg radio path (Figure 1). As diagnostic signals we used the carriers of broadcasting transmitters located near London (geographical coordinates 52oN, 0oE) at frequencies 9410 and 12,095 kHz. The reception of the diagnostic waves scattered from artificial field-aligned irregularities was made by a Doppler spectral method in St. Petersburg (59.6oN, 30.4oE) at a distance of about 1200 km from the Tromsö heater. The receiving antenna was directed toward Tromsö. Spectral processing of the HF diagnostic signals was made by the fast Fourier transform (FFT) method. The frequency analysis band was 33 Hz and the 512 coefficients used in the FFT allowed a frequency resolution of 0.064 Hz.

|
| Figure 3 |
An analysis of Tromsö dynasonde ionograms
as well as EISCAT UHF radar data
during the HF pumping experiment on 17 February 1996 shows the presence of
an intense sporadic
Es layer at the altitudes between 100 and 130 km,
with a maximum plasma frequency
4.1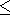 foEs
foEs
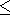 4.5 MHz.
The detailed examination of Tromsö dynasonde
ionograms as well as the
simulation of the geometry of the diagnostic HF signals scattered from AFAI in
the
E region were performed by
Blagoveshchenskaya et al. [1999].
One can
conclude that the
Es region of the auroral ionosphere was actually the
region where the powerful HF radio waves were reflected. This leads to a
generation of intense artificial
field-aligned irregularities in the
ionospheric
E region responsible for the scattering of the diagnostic HF
signals on the London-Tromsö-St. Petersburg
path. The HF radar measurements
(12,095 and 9410 kHz) were sensitive to AFAI having a wavelength of 12 and 15 m
across the geomagnetic field lines. Note that AFAI scale lengths from 1 to 7 m
were observed in the auroral
E region by
Djuth et al. [1985]
and
Noble et al. [1987].
The thermal resonance instability occurring at the upper
hybrid level is believed to be the most likely candidate
for the excitation of
AFAI in the
E region.
The generation of AFAI
should be limited to a region about the size of the heater beam in the
ionosphere. Nonetheless,
the real size of the heated region in the auroral
E layer is significantly larger than the area determined from the heater
beam.
From 46.9 MHz radar observations it was found that the heated spot averaged
between 80 and 90 km at the altitude of about 100 km during
Tromsö HF
pumping experiment in the nightside auroral
E region
[Djuth et al., 1985].
4.5 MHz.
The detailed examination of Tromsö dynasonde
ionograms as well as the
simulation of the geometry of the diagnostic HF signals scattered from AFAI in
the
E region were performed by
Blagoveshchenskaya et al. [1999].
One can
conclude that the
Es region of the auroral ionosphere was actually the
region where the powerful HF radio waves were reflected. This leads to a
generation of intense artificial
field-aligned irregularities in the
ionospheric
E region responsible for the scattering of the diagnostic HF
signals on the London-Tromsö-St. Petersburg
path. The HF radar measurements
(12,095 and 9410 kHz) were sensitive to AFAI having a wavelength of 12 and 15 m
across the geomagnetic field lines. Note that AFAI scale lengths from 1 to 7 m
were observed in the auroral
E region by
Djuth et al. [1985]
and
Noble et al. [1987].
The thermal resonance instability occurring at the upper
hybrid level is believed to be the most likely candidate
for the excitation of
AFAI in the
E region.
The generation of AFAI
should be limited to a region about the size of the heater beam in the
ionosphere. Nonetheless,
the real size of the heated region in the auroral
E layer is significantly larger than the area determined from the heater
beam.
From 46.9 MHz radar observations it was found that the heated spot averaged
between 80 and 90 km at the altitude of about 100 km during
Tromsö HF
pumping experiment in the nightside auroral
E region
[Djuth et al., 1985].
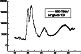
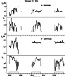
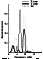
The most interesting peculiarity of the field-aligned scattered HF signals is the appearance of the oscillatory variations in the Doppler shift, fd, with periods about 115 s during the first heating cycle from 2000 to 2004 UT. The amplitude of this wave-like process was determined as the maximum fluctuation of fd during the heating cycle ( fd max -fd min ), and was about 1.1 Hz. The periods in fd of the wave-like processes mentioned fall within the range of Pi2 geomagnetic pulsations. In the subsequent HF pumping cycles, no variations of fd were observed in the scattered signals. The direct HF signal from London to St. Petersburg does not exhibit any such variations during the whole interval analyzed.

|
| Figure 4 |
 B drift, from Doppler measurement
data
(fd max=1,1 Hz,
f=12,095 kHz)
the electric field ranges up to about 4 mV m
-1.
Therefore
EX/BY ratio is of the order of
300 km s
-1,
which is in agreement with the Alfvén
velocity at the altitude of the electron density maximum of the ionosphere.
B drift, from Doppler measurement
data
(fd max=1,1 Hz,
f=12,095 kHz)
the electric field ranges up to about 4 mV m
-1.
Therefore
EX/BY ratio is of the order of
300 km s
-1,
which is in agreement with the Alfvén
velocity at the altitude of the electron density maximum of the ionosphere.
|
| Figure 5 |
The most likely explanation for the wave-like behavior of
fd (electric
field) is Alfvén waves, while the spectral
power variations
Sp (intensity of back-scattered signals) are due to the
fast mode MHD waves as
shown by
Yeoman et al. [1991]
from coherent HF radar data.
Recall that the nonlinear interaction between the ionospheric plasma and
powerful HF radio waves leads to the modification of the ionospheric
conductivities, and therefore current distribution, due to changes of the
electron temperature as well as electron density. In view of the fact that
electron density changes have a comparatively long time constant (of the order
of a minute), significant electron density changes are possible only for a
long heater-on period. However, in this case the conductivity disturbance is
much stronger, than that of temperature changes, due to all conductivity
elements (Hall and Pedersen conductivities) are modified
[Stubbe, 1996].
Results of calculations for long-period heating cycles have
shown that the heater-induced conductivity perturbations are of the order
DS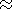 2S [Lyatsky et al., 1996].
A disturbed ionospheric current distribution implies a magnetic field
disturbance. Therefore the study of the polarization of the magnetic field
variations in the
X and
Y components provides a way of getting the information
about disturbances of ionospheric currents.
2S [Lyatsky et al., 1996].
A disturbed ionospheric current distribution implies a magnetic field
disturbance. Therefore the study of the polarization of the magnetic field
variations in the
X and
Y components provides a way of getting the information
about disturbances of ionospheric currents.
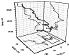
|
| Figure 6 |
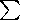 sH/
sH/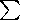 sP.
Note that when the
sP.
Note that when the
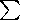 sH/
sH/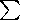 sP
ratio changes
during the heater-on period, a rotation of the
polarization vector occurs. If this ratio is kept constant, the polarization
is linear
[Lyatsky et al., 1996].
Therefore the appearance of the loops
in the polarization surfaces are indicative for a strong
sP
ratio changes
during the heater-on period, a rotation of the
polarization vector occurs. If this ratio is kept constant, the polarization
is linear
[Lyatsky et al., 1996].
Therefore the appearance of the loops
in the polarization surfaces are indicative for a strong
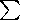 sH/
sH/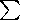 sP
ratio changes and consequently the ionospheric currents. The
most strong changes were observed during the first heating cycle
(2000-2004 UT),
when a composite loop occurred. In the second heater-on period the
more simple loop was observed in the polarization surfaces.
Also, at last, in
the third heater-on period (2020-2024 UT) a small loop took place only in
beginning of the pumping cycle. Hence, the results obtained are experimental
evidences for a local modification, by powerful HF radio waves, of the auroral
ionospheric currents.
sP
ratio changes and consequently the ionospheric currents. The
most strong changes were observed during the first heating cycle
(2000-2004 UT),
when a composite loop occurred. In the second heater-on period the
more simple loop was observed in the polarization surfaces.
Also, at last, in
the third heater-on period (2020-2024 UT) a small loop took place only in
beginning of the pumping cycle. Hence, the results obtained are experimental
evidences for a local modification, by powerful HF radio waves, of the auroral
ionospheric currents.
Coordinated observations of ULF wave activity in the 110-120 s range from HF bistatic Doppler measurements on the London-Tromsö-St. Petersburg path and IMAGE magnetometer network were performed in an HF modified ionosphere on 17 February 1996. The experiment was unusual in that a strong auroral Es layer was pumped during the initiation stage of the background upward field-aligned currents (FAC) of the substorm current system. The analysis of the HF Doppler data shows that there is a clear evidence of the excitation of intense artificial field-aligned irregularities (AFAI) in the Es layer (see Figure 3). On the other hand, one can notice a strong modification of the ionospheric currents by powerful HF radio waves in the Tromsö magnetic field variation data (see Figure 6). Moreover, the upper hybrid resonance level where the heater-induced irregularities are excited is near the altitudes of the heater-enhanced conductivity region.
It is well known [Kamide and Baumjohann, 1993; Raspopov, 1968; Raspopov and Troitskaya, 1974; Yeoman et al., 1991] that a substorm intensification can be accompanied by the generation of Pi2 magnetic pulsations in the range 90-150 s. Pi2 pulsations consist of an auroral zone Alfvén wave and a lower latitude compressional mode, possibly due to a cavity mode wave source. The auroral zone Pi2 polarization pattern exhibits clockwise (CW) polarization that undergoes a reversal to become anticlockwise (ACW) at lower latitudes [Yeoman et al., 1991]. In our case, the ionospheric and magnetic pulsations observed during the first heating cycle could be the signatures of Pi2 pulsations. To study this point, the magnetic field variations in the X and Y components were considered from all of the magnetometers in the IMAGE network, as shown in Figure 1. The examination of the unfiltered and filtered (between 120 and 80 s) X and Y component variation data presented by Blagoveshchenskaya et al. [1998b] shows a 180o phase change of the X component in latitude between BJN and SOR stations located to the north from TRO station. Moreover, this phase change started 1 min before the Tromsö HF heating facility was turned on.
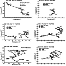
|
| Figure 7 |
|
| Figure 8 |
What is the nature of the observed ULF wave activity during the first heating
cycle? In our opinion the most plausible candidate for the generation
mechanism of the ionospheric and magnetic pulsations of the Pi2 type is the
following: The powerful HF radio wave in the lower ionosphere locally modifies
the ionospheric conductivity
[Lyatsky et al., 1996;
Stubbe, 1996].
It
was shown by
Lyatsky and Maltsev [1983],
Kan and Sun [1985],
Lysak [1990],
and
Borisov et al. [1996]
that the region of enhanced
ionospheric conductivity will be polarized by the background electric field
and the polarization electric field propagates into the magnetosphere along
the magnetic field lines in the form of an outgoing Alfvén
wave. The
problem of the Alfvén wave generation
over a circular inhomogeneity of the
disturbed conductivity in the background field-aligned current region has been
considered by
Kozlovsky and Lyatsky [1997].
Recall that calculated conductivity perturbations range up
to about
DS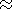 2S for long-period heating cycles.
2S for long-period heating cycles.
It was shown that over the region of the enhanced ionospheric conductivity, an additional field-aligned current of the outgoing Alfvén wave is directed in the same sense as the background FAC. When the outgoing Alfvén wave reaches the magnetosphere, it will be reflected. Multiple bounces of the wave can provide an electromagnetic coupling between the ionosphere and magnetosphere and lead to magnetic and electric field oscillations. The other possible mechanism for the Alfvén wave generation is a field-aligned current-driven instability which starts earlier over a patch of the heater-enhanced conductivity [Zhulin et al., 1978]. This leads to the positive feedback in the magnetosphere-ionosphere system and the further growth of the upward background field-aligned currents during the initiation stage of the substorm current system. The mechanism mentioned above for the Alfvén wave excitation can be realized in the E region during the initiation stage of the FAC system. That is the reason that the substorm onset controls the occurrence of the heater-induced Alfvén wave and therefore the strong modification of the Y component of magnetic field variations. Taking into account that the Alfvén wave travel time between the ionosphere and magnetosphere for the Tromsö L shell is ~60 s, the magnetic and electric field oscillations must have a period of 120 s, which is close to our observed results. Note that the amplitude of the Y component of the magnetic field variations at Tromsö was not damped during the first heating cycle and the pulsations disappeared 1 min after the heater was turned off (see Figure 4). This corresponds to the travel time of the reflected heater-induced Alfvén wave from the magnetosphere to the ionosphere after the heater was turned off.
We therefore suggest that the outgoing Alfvén wave is generated from a heater-induced inhomogeneity of enhanced conductivity. The field-aligned current of this wave is directed so that there is a slight increase in the upward directed field-aligned current. When the Alfvén wave reflects from the magnetosphere, its downward direction acts to decrease the background current. Therefore the wave-associated currents can modulate the upward background field-aligned currents produced by the substorm surge form. The period of these pulsations is determined by the Alfvén wave travel time between the ionosphere and magnetosphere. It should be noted that less pronounced magnetic pulsations were observed at the SOR, MAS and KEV stations. These observations strongly suggest that the above mentioned stations were located in the area of the upward field-aligned current.
We conclude that under initiation stage of the FAC system, HF pumping can modify the compressional mode of Pi2 magnetic pulsations by modulating substorm-produced field-aligned currents. The mechanism is the perturbation of those currents by heater-induced primary and reflected Alfvén waves. The excitation of the Alfvén wave, possibly due to the field-aligned current-driven instability, over a region of the heater-enhanced conductivity in the E region is in a good agreement with estimation of the EX/BY ratio which is of the order of the Alfvén velocity at the altitude of the electron density maximum in the ionosphere.
The strong modification of magnetic pulsations confirmed as follows: (1) a reversal of the polarization pattern from anticlockwise (ACW) to clockwise (CW) polarization one minute after the HF heater was turned on, observed in the longitudinally limited area near TRO latitude; (2) different periods in the X and Y magnetic components; and (3) the close correlation between Doppler frequency shifts and Y magnetic component but not X component as it is usually observed for the natural compressional mode of Pi2 magnetic pulsations. We emphasize that the geophysical conditions (the onset of the substorm activation, the initiation phase of the background upward field-aligned currents, the presence of the Es layer) during HF pumping experiment control significantly the occurrence of the heater-induced Alfvén wave.
Belenov, A. F., L. M. Erukhimov, P. V. Ponomarenko, and Y. M. Yampolski, Interaction between artificial ionospheric turbulence and geomagnetic pulsations, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 59, 2367, 1997.
Blagoveshchenskaya, N. F., and O. A. Troshichev, Ionospheric phenomena produced by modification experiments, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 58, 397, 1996.
Blagoveshchenskaya, N. F., V. A. Bubnov, and V. I. Shelukhin, Experimental investigations of HF signal characteristics at short radio paths during ionospheric modification by powerful HF radio waves, Izv. VUZov Radiofiz. (in Russian), 35, 24, 1992.
Blagoveshchenskaya, N. F., A. D. Andreev, and V. A. Kornienko, Ionospheric wave processes during HF heating experiments, Adv. Space Res., 15 (12), 45, 1995.
Blagoveshchenskaya, N. F., M. Yu. Chernyshev, and V. A. Kornienko, Excitation of small-scale waves in the F region of the ionosphere by powerful HF radio waves, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 60, 1225, 1998a.
Blagoveshchenskaya, N. F., V. A. Kornienko, A. V. Petlenko, A. Brekke, and M. T. Rietveld, Geophysical phenomena during an ionospheric modification experiment at Tromsö, Norway, Ann. Geophys., 16, 1212, 1998b.
Blagoveshchenskaya, N. F., V. A. Kornienko, A. Brekke, M. T. Rietveld, M. Kosch, T. D. Borisova, and M. V. Krylosov, Phenomena observed by HF long-distance tools in the HF modified auroral ionosphere during magnetospheric substorm, Radio Sci., 34, 715, 1999.
Borisov, N., A. Gurevich, K. Papadopoulos, and C. L. Chang, Controlled generation of coherent low frequency ULF/ELF/ VLF, Radio Sci., 31, 859, 1996.
Djuth, F. T., et al., Observations of E region irregularities generated at auroral latitudes by a high-power radio wave, J. Geophys. Res., 90, 12,293, 1985.
Inhester, B., W. Baumjohann, R. A. Greenwald, and E. Nielsen, Joint two-dimensional observations of ground magnetic and ionospheric electric fields associated with auroral zone currents, 3, Auroral zone currents during the passage of westward travelling surge, J. Geophys., 49, 155, 1981.
Kamide, Y., and W. Baumjohann, Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Coupling, 178 pp., Springer-Verlag, New York, 1993.
Kan, J. R., and W. Sun, Simulation of the westward travelling surge and Pi2 pulsations during substorms, J. Geophys. Res., 90, 10,911, 1985.
Kozlovsky, A. E., and W. B. Lyatsky, Alfvén wave generation by disturbance of ionospheric conductivity in the field-aligned current region, J. Geophys. Res., 102, 17,297, 1997.
Lyatsky, W. B. and Yu. P. Maltsev, The Magnetosphere-Ionosphere Interaction (in Russian), 192 pp., Nauka, Moscow, 1983.
Lyatsky, W., E. G. Belova, and A. B. Pashin, Artificial magnetic pulsation generation by powerful ground-based transmitter, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 58, 407, 1996.
Lysak, R. L., Electrodynamic coupling of the magnetosphere and ionosphere, Space Sci. Rev., 52, 33, 1990.
Noble, S. T., et al., Multiple frequency radar observations of high-latitude E region irregularities in the HF modified ionosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 92, 13,613, 1987.
Raspopov, O. M., About possible mechanism of the generation of Pi2 magnetic pulsations, Geomagn. Aeron. (in Russian), 8, 326, 1968.
Raspopov, O. M., and V. A. Troitskaya, Development of substorm in magnetic pulsations, in High-Latitude Geophysical Phenomena (in Russian), pp. 234-247, Nauka, Leningrad, 1974.
Stubbe, P., Review of ionospheric modification experiments at Tromsö, J. Atmos. Terr. Phys., 58, 349, 1996.
Viljanen, A., and L. Häkkinen, IMAGE magnetometer network, in Satellite-Ground Based Coordination Sourcebook, edited by M. Lockwood, M. N. Wild, and H. J. Opgenoorth, ESA SP-1198, pp. 111-117, Eur. Space Agency Spec. Publ., 1997.
Yeoman, T. K., M. Lester, D. K. Milling, and D. Orr, Polarization, propagation and MHD wave modes of Pi2 pulsations: SABRE/SAMNET results, Planet. Space Sci., 39, 983, 1991.
Yeoman, T. K., D. M. Wright, T. R. Robinson, J. A. Davies, and M. T. Rietveld, High spatial and temporal resolution observations of an impulse-driven field line resonance in radar backscatter artificially generated with the Tromsö heater, Ann. Geophys., 15, 634, 1997.
Zhulin, I. A., V. M. Mishin, E. V. Mishin, and V. M. Chmyrev, Possibility of artificial localization of a magnetospheric substorm, Geomagn. Aeron. (Engl. Transl.), 18, 377, 1978.