1. Introduction
[2] The paper describes the mathematical foundation of the effective
algorithm of calculations of components of electric and magnetic
field intensity in the 5-30 kHz range generated by a short
antenna located at some altitude
d 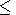 50 km over the Earth
surface. The distance to the observational point
R
50 km over the Earth
surface. The distance to the observational point
R 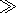 d and
R
d and
R 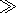 l (where
l is the wavelength of the
electromagnetic field in the vacuum). The main mechanism of VLF
propagation
[Budden, 1961a, 1961b;
Krasnushkin and Yablochkin, 1963;
Makarov et al., 1993;
Wait, 1962],
at which the field
is presented as an expansion in terms of modes (eigenfunctions of
the discrete spectrum of the lateral operator) propagating at the
shortest way between the corresponding points, is taken into
account.
l (where
l is the wavelength of the
electromagnetic field in the vacuum). The main mechanism of VLF
propagation
[Budden, 1961a, 1961b;
Krasnushkin and Yablochkin, 1963;
Makarov et al., 1993;
Wait, 1962],
at which the field
is presented as an expansion in terms of modes (eigenfunctions of
the discrete spectrum of the lateral operator) propagating at the
shortest way between the corresponding points, is taken into
account.
[3] The receiving antenna is short and may be located at some height
da 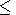 50 km or some depth
da < 0, assuming that
|da|
50 km or some depth
da < 0, assuming that
|da| 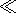 R. The algorithm is based on the path
approximation at which possible changes in the waveguide
properties along the geodesic line are taken into account, but
their possible changes in the lateral direction being neglected.
R. The algorithm is based on the path
approximation at which possible changes in the waveguide
properties along the geodesic line are taken into account, but
their possible changes in the lateral direction being neglected.

Powered by TeXWeb (Win32, v.2.0).
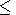 50 km over the Earth
surface. The distance to the observational point
R
50 km over the Earth
surface. The distance to the observational point
R 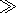 d and
R
d and
R 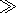 l (where
l is the wavelength of the
electromagnetic field in the vacuum). The main mechanism of VLF
propagation
[Budden, 1961a, 1961b;
Krasnushkin and Yablochkin, 1963;
Makarov et al., 1993;
Wait, 1962],
at which the field
is presented as an expansion in terms of modes (eigenfunctions of
the discrete spectrum of the lateral operator) propagating at the
shortest way between the corresponding points, is taken into
account.
l (where
l is the wavelength of the
electromagnetic field in the vacuum). The main mechanism of VLF
propagation
[Budden, 1961a, 1961b;
Krasnushkin and Yablochkin, 1963;
Makarov et al., 1993;
Wait, 1962],
at which the field
is presented as an expansion in terms of modes (eigenfunctions of
the discrete spectrum of the lateral operator) propagating at the
shortest way between the corresponding points, is taken into
account. R. The algorithm is based on the path
approximation at which possible changes in the waveguide
properties along the geodesic line are taken into account, but
their possible changes in the lateral direction being neglected.
R. The algorithm is based on the path
approximation at which possible changes in the waveguide
properties along the geodesic line are taken into account, but
their possible changes in the lateral direction being neglected.