3. Power of the Sector Structure of the Large-Scale
Magnetic Field SSPD(t)
[14] In studies of the rotation of the sector structure of the
solar magnetic field, the rotation index
SSPD(t) was introduced
by Vasil'eva et al. [2002]. It is determined by
the sum of the spectral density of the power of the magnetic field
sector structure. To find the spectral density of the power, we
used the Fourier transformation. The Fourier coefficients for each
realization can be presented in the form
|
|
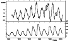
Figure 4
|
where the function
y(t) is given in
N discrete points of the
segment
[0, T] with the step of realization
Dt=T/N.
The spectral density is found as
where
and
Let us introduce the index of the sum of the spectral density of
the power
SSPD. To obtain this index, we sum over the spectral
density
S for the periods of oscillations
T 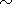 6-15 days
This range corresponds to the periods of oscillations for the 4-
and the 6-sector structures of the large-scale magnetic field.
Evidently, it is an indication of the presence or absence of
different types of the magnetic field sector structure. Comparison
of the
SSPD(t)
index with the index of Wolf numbers
W(t) for
the period from 1904 to 2005 has revealed that the 11-year
activity cycles of the magnetic field sector structure
SSPD(t) are shifted by 5-6 years and precede in amplitude and phase the
11-year cycles of the Wolf numbers (Figure 4). This implies that
the sector structure of the solar magnetic field actively
participates in the magnetic field generation, and therefore it is
one of the basic types of motion. The correlation coefficient
between the maximums of parameters
Wmax and
SSPDmax is
equal to
R=0.96. The regression formula can be presented in the
form
Wmax = 195 Lmax - 143. The mean square error
comprised
s=
6-15 days
This range corresponds to the periods of oscillations for the 4-
and the 6-sector structures of the large-scale magnetic field.
Evidently, it is an indication of the presence or absence of
different types of the magnetic field sector structure. Comparison
of the
SSPD(t)
index with the index of Wolf numbers
W(t) for
the period from 1904 to 2005 has revealed that the 11-year
activity cycles of the magnetic field sector structure
SSPD(t) are shifted by 5-6 years and precede in amplitude and phase the
11-year cycles of the Wolf numbers (Figure 4). This implies that
the sector structure of the solar magnetic field actively
participates in the magnetic field generation, and therefore it is
one of the basic types of motion. The correlation coefficient
between the maximums of parameters
Wmax and
SSPDmax is
equal to
R=0.96. The regression formula can be presented in the
form
Wmax = 195 Lmax - 143. The mean square error
comprised
s=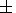 11 W. Unfortunately, the peak of this
function is not achieved yet. Therefore the forecast for cycle 24
is not possible.
11 W. Unfortunately, the peak of this
function is not achieved yet. Therefore the forecast for cycle 24
is not possible.

Powered by TeXWeb (Win32, v.2.0).
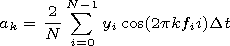
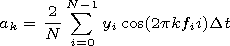

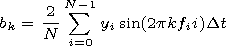
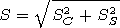
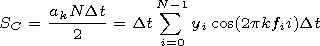
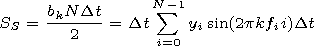
 6-15 days
6-15 days
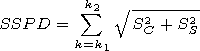
 11 W. Unfortunately, the peak of this
function is not achieved yet. Therefore the forecast for cycle 24
is not possible.
11 W. Unfortunately, the peak of this
function is not achieved yet. Therefore the forecast for cycle 24
is not possible.
