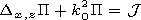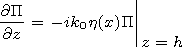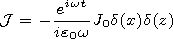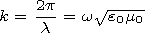2. Formulation of the Problem
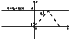
|
|
Figure 1
|
[4] We consider an infinite threadlike source of the current with the
density
j:
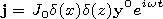 | (1) |
located parallel with the
Oy axis (see Figure 1). Here
J0 is
the source amplitude. We assume that the source of electromagnetic
waves (1) is located in the lower vacuum semispace
z 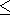 h limited from above by a plain boundary
z = h with the
one-dimensionally inhomogeneous impedance
h(x) = h0 + h1(x) normalized to
(m0/ e0)1/2 and
modeling the presence of an internal gravity wave at the
ionosphere lower boundary. Here Re
(h(x))
h limited from above by a plain boundary
z = h with the
one-dimensionally inhomogeneous impedance
h(x) = h0 + h1(x) normalized to
(m0/ e0)1/2 and
modeling the presence of an internal gravity wave at the
ionosphere lower boundary. Here Re
(h(x)) 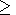 0,
h0 = const, and
max(|h1|) < |h0|.
The horizontal scale
lg of the irregularity we assume to
be much larger than the wavelength
l. Therefore we neglect
the depolarization [see Al'pert et al., 1953].
0,
h0 = const, and
max(|h1|) < |h0|.
The horizontal scale
lg of the irregularity we assume to
be much larger than the wavelength
l. Therefore we neglect
the depolarization [see Al'pert et al., 1953].
[5] The vertical component of the Hertz vector
P (which can be
used to express all the components of the electromagnetic field)
satisfies the wave equation
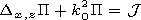 | (2) |
with the boundary condition
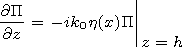 | (3) |
and also the radiation condition. Here
Dx,z is the
two-dimensional Laplace operator in the Cartesian coordinate
system
(x,y,z), and the right-hand side of equation (2) is
written in the form
below we will omit the time multiplier
ei wt.

Powered by TeXWeb (Win32, v.2.0).


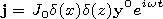
 h limited from above by a plain boundary
z = h with the
one-dimensionally inhomogeneous impedance
h(x) = h0 + h1(x) normalized to
(m0/ e0)1/2 and
modeling the presence of an internal gravity wave at the
ionosphere lower boundary. Here Re
(h(x))
h limited from above by a plain boundary
z = h with the
one-dimensionally inhomogeneous impedance
h(x) = h0 + h1(x) normalized to
(m0/ e0)1/2 and
modeling the presence of an internal gravity wave at the
ionosphere lower boundary. Here Re
(h(x)) 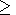 0,
h0 = const, and
max(|h1|) < |h0|.
The horizontal scale
lg of the irregularity we assume to
be much larger than the wavelength
l. Therefore we neglect
the depolarization [see Al'pert et al., 1953].
0,
h0 = const, and
max(|h1|) < |h0|.
The horizontal scale
lg of the irregularity we assume to
be much larger than the wavelength
l. Therefore we neglect
the depolarization [see Al'pert et al., 1953].