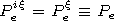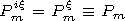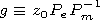2. Formulation and Construction of the Solution
[6] The Earth-ionosphere waveguide is modeled by a spherical cavity
characterized by the properties of the free space. In the
geocentric spherical coordinate system
r,q, j, the
axis
q=0 goes through the emitter located in the ionosphere
in point 1 with coordinates
r = b and
q= 0. The ground
( r a ) and the ionosphere ( r
a ) and the ionosphere ( r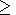 d ) are considered as
inhomogeneous media depending on
r and
q. Point electric
and magnetic dipoles oriented along the unit vectors
ex ( x = r, q, j ) and oscillating according to
exp(-iwt) are used as the field sources ( w is the
angular frequency). The IS system of units is used. Our aim is to
find the electric
E and magnetic
H fields in a point 2
with coordinates
r, q located in the waveguide cavity.
d ) are considered as
inhomogeneous media depending on
r and
q. Point electric
and magnetic dipoles oriented along the unit vectors
ex ( x = r, q, j ) and oscillating according to
exp(-iwt) are used as the field sources ( w is the
angular frequency). The IS system of units is used. Our aim is to
find the electric
E and magnetic
H fields in a point 2
with coordinates
r, q located in the waveguide cavity.
[7] The generalized reciprocity theorem for magnetoactive medium makes
it possible to find components of the fields excited in the
waveguide cavity by ionospheric dipoles using components of the
fields excited in the ionosphere by the dipoles located in the
waveguide cavity:
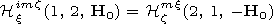 | (1) |
Here
Hp  z0 Hp,
p=x, z,
where
z0=120 p [Ohm]
is the characteristic impedance of free space. The indices
e and
m at the field components refer to the electric and magnetic
dipoles, respectively. For example,
Exiez(1, 2, H0) and
Hxiez(1, 2, H0) are the
x components of the fields excited in the waveguide
cavity in point 2 by the electric dipole with the dipole moment
Peiz located in the ionosphere in point 1 and
oriented along the unit vector
ez;
Ezex(2, 1,- H0) and
Hzex (2, 1, - H0) are the
z components of the
electric and magnetic fields, respectively, excited in point 1 in
the ionosphere at the geomagnetic field
- H0 by an
auxiliary electrical dipole with the moment
Pex located in point 2 and oriented along the unit vector
ex ( x,
z =
r, q,
j ). In expressions (1) it
is assumed that
z0 Hp,
p=x, z,
where
z0=120 p [Ohm]
is the characteristic impedance of free space. The indices
e and
m at the field components refer to the electric and magnetic
dipoles, respectively. For example,
Exiez(1, 2, H0) and
Hxiez(1, 2, H0) are the
x components of the fields excited in the waveguide
cavity in point 2 by the electric dipole with the dipole moment
Peiz located in the ionosphere in point 1 and
oriented along the unit vector
ez;
Ezex(2, 1,- H0) and
Hzex (2, 1, - H0) are the
z components of the
electric and magnetic fields, respectively, excited in point 1 in
the ionosphere at the geomagnetic field
- H0 by an
auxiliary electrical dipole with the moment
Pex located in point 2 and oriented along the unit vector
ex ( x,
z =
r, q,
j ). In expressions (1) it
is assumed that
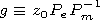 | (2) |

Powered by TeXWeb (Win32, v.2.0).
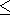 a ) and the ionosphere ( r
a ) and the ionosphere ( r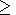 d ) are considered as
inhomogeneous media depending on
r and
q. Point electric
and magnetic dipoles oriented along the unit vectors
ex ( x = r, q, j ) and oscillating according to
exp(-iwt) are used as the field sources ( w is the
angular frequency). The IS system of units is used. Our aim is to
find the electric
d ) are considered as
inhomogeneous media depending on
r and
q. Point electric
and magnetic dipoles oriented along the unit vectors
ex ( x = r, q, j ) and oscillating according to
exp(-iwt) are used as the field sources ( w is the
angular frequency). The IS system of units is used. Our aim is to
find the electric
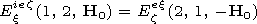
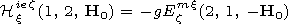
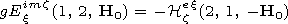
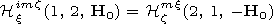
 z0 Hp,
p=x, z,
where
z0=120 p [Ohm]
is the characteristic impedance of free space. The indices
e and
m at the field components refer to the electric and magnetic
dipoles, respectively. For example,
Exiez(1, 2, H0) and
Hxiez(1, 2, H0) are the
x components of the fields excited in the waveguide
cavity in point 2 by the electric dipole with the dipole moment
Peiz located in the ionosphere in point 1 and
oriented along the unit vector
z0 Hp,
p=x, z,
where
z0=120 p [Ohm]
is the characteristic impedance of free space. The indices
e and
m at the field components refer to the electric and magnetic
dipoles, respectively. For example,
Exiez(1, 2, H0) and
Hxiez(1, 2, H0) are the
x components of the fields excited in the waveguide
cavity in point 2 by the electric dipole with the dipole moment
Peiz located in the ionosphere in point 1 and
oriented along the unit vector