3. Conclusions
[21] Summarizing the results of the experimental
[Klimov et al., 1982;
Mishin et al., 1991]
and theoretical studies
[Pavlov, 1996, 2002b],
one can conclude that the field distribution in the problem on the
motion of a strong shock wave in weakly ionized plasma is
characterized by several dimensionless parameters. The most
significant of them are the Mach number
M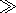 1, the ion-sonic
Mach number
2>Mi >1, the ionization degree
( d
1, the ion-sonic
Mach number
2>Mi >1, the ionization degree
( d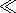 1 ), and the
ratio of the temperatures of electrons and neutral particles
B
1 ), and the
ratio of the temperatures of electrons and neutral particles
B Te/Ti
Te/Ti 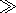 1.
The ion-sonic Mach number is related to the Mach
number by the formula
Mi = M(g/B)1/2, where
g is the ratio
between the specific heat capacities of the neutral gas. Because of
strong nonlinearity and a dispersion, there appears a significantly
nonmonotonic dependence of the field amplitude on the velocity of
the shock wave when the condition
Mi
1.
The ion-sonic Mach number is related to the Mach
number by the formula
Mi = M(g/B)1/2, where
g is the ratio
between the specific heat capacities of the neutral gas. Because of
strong nonlinearity and a dispersion, there appears a significantly
nonmonotonic dependence of the field amplitude on the velocity of
the shock wave when the condition
Mi 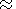 1.6
1.6 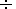 2 is fulfilled. In the
resonant regions, the propagation of the shock wave in the weakly
ionized plasma is determined by the ion-sonic Mach number.
Under the condition
M = const, but at different values of the
B parameter, the flowing around of the body will be different. The
obligatory condition for the resonance occurrence is the
requirement
Mi
2 is fulfilled. In the
resonant regions, the propagation of the shock wave in the weakly
ionized plasma is determined by the ion-sonic Mach number.
Under the condition
M = const, but at different values of the
B parameter, the flowing around of the body will be different. The
obligatory condition for the resonance occurrence is the
requirement
Mi 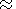 1.6
1.6 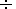 2.
This is a peculiarity of the "plasma
effect".
2.
This is a peculiarity of the "plasma
effect".
[22] It should be noted that a correct modeling of plasma experiments in
laboratory conditions present a complicated problem because of the
contamination of the working gas by the products of electrode
erosion and also presence of solid particles in the gas flowing out
of the nozzle. The latter may be ice crystals, pieces of films of
oxides from the incoming tubes, and dust from the air. Such
contaminations are badly controlled especially in the experiments
in aerodynamic tubes. In a plasma-dynamic experiment, a
formation in the flow of qualitatively new medium (dust plasma
containing microscopic charged particles) is possible. In such
plasma, appearance of a complex of even more complicated
nonlinear resonance effects determined by many parameters is
possible [Pavlov, 2002b].

Powered by TeXWeb (Win32, v.2.0).
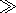 1, the ion-sonic
Mach number
2>Mi >1, the ionization degree
( d
1, the ion-sonic
Mach number
2>Mi >1, the ionization degree
( d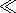 1 ), and the
ratio of the temperatures of electrons and neutral particles
B
1 ), and the
ratio of the temperatures of electrons and neutral particles
B Te/Ti
Te/Ti 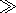 1.
The ion-sonic Mach number is related to the Mach
number by the formula
Mi = M(g/B)1/2, where
g is the ratio
between the specific heat capacities of the neutral gas. Because of
strong nonlinearity and a dispersion, there appears a significantly
nonmonotonic dependence of the field amplitude on the velocity of
the shock wave when the condition
Mi
1.
The ion-sonic Mach number is related to the Mach
number by the formula
Mi = M(g/B)1/2, where
g is the ratio
between the specific heat capacities of the neutral gas. Because of
strong nonlinearity and a dispersion, there appears a significantly
nonmonotonic dependence of the field amplitude on the velocity of
the shock wave when the condition
Mi 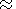 1.6
1.6 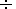 2 is fulfilled. In the
resonant regions, the propagation of the shock wave in the weakly
ionized plasma is determined by the ion-sonic Mach number.
Under the condition
M = const, but at different values of the
B parameter, the flowing around of the body will be different. The
obligatory condition for the resonance occurrence is the
requirement
Mi
2 is fulfilled. In the
resonant regions, the propagation of the shock wave in the weakly
ionized plasma is determined by the ion-sonic Mach number.
Under the condition
M = const, but at different values of the
B parameter, the flowing around of the body will be different. The
obligatory condition for the resonance occurrence is the
requirement
Mi 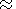 1.6
1.6 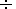 2.
This is a peculiarity of the "plasma
effect".
2.
This is a peculiarity of the "plasma
effect".