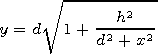
[4] In this paper the problem of diffraction of electromagnetic waves in the Earth-ionosphere waveguide is solved, the waveguide being modeled by a plain waveguide with a vertical barrier. The walls and barrier are infinitely conducting.
[5] In the beginning, the problem of diffraction in a plain waveguide with a thin wall and smoothly curved upper wall (that corresponds to the presence of a smooth disturbance in the ionosphere) is solved with the help of SIM. Taking into account some introduced limitation of the problem parameters, the zero and first approximations are found. Then a two-dimensional waveguide with a barrier and plain upper wall (undisturbed ionosphere) is considered. The problem is solved using MQGF. This makes it possible to get rid of some limitations having appeared at the use of SIM. The comparison of the results of application of these methods makes it possible to conclude that the input of smooth disturbances of the ionosphere into the electromagnetic field is insignificant as compared to the influence of local angular irregularities on the Earth surface.
[6] Now we come to consideration of a two-dimensional waveguide with a curved upper wall. A vertical barrier with a height h is located in the point ( 0,0 ). The upper wall of the waveguide is described by
 |

|
| Figure 1 |
 d (Figure 1).
d (Figure 1).

Powered by TeXWeb (Win32, v.2.0).