2. Installation Parameters and Method of Studies
[4] The method of partial reflections is one of the ground-based
methods of quantitative studies of the flare effects in the lower
ionosphere
[Mitra, 1974].
The characteristics and structural scheme
of the measuring partial reflections installation of PGI were described
by
Tereshchenko et al. [2003].
The installation is located in the
vicinity of Tumanny town of the Murmansk Region (69.0o N,
35.7o E). The observations were conducted at frequencies of 2.65-2.78 MHz
at the pulse power of the transmitter about 60 kW and
pulse duration of 15
m s. The reception of the scattered signals was
conducted by receiving-transmitting antenna with the directivity
diagram of
19 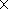 22o at the half-power level. Two circular
polarizations were received in turn and were amplified by the receiver
with the band of 40 kHz. The registration of the signal amplitudes
was performed in the height interval 50-146 km. The step of the
data reading was 1.5 km. The receiving instrumentation was
equipped by a quick-operating multichannel analog-digital
transformer and computer for reception, processing, and analysis of
the data. The amplitudes of the ordinary and extraordinary
components of the signal were averaged over every minute at all
registered altitudes. These data were used for the general estimation
of the observation results and then were averaged over time intervals
5-15 min. Using the averaged data, the electron concentration
profile
Ne(h) was calculated by the method of differential
absorption of radio waves described by
Belikovich et al. [2003a].
22o at the half-power level. Two circular
polarizations were received in turn and were amplified by the receiver
with the band of 40 kHz. The registration of the signal amplitudes
was performed in the height interval 50-146 km. The step of the
data reading was 1.5 km. The receiving instrumentation was
equipped by a quick-operating multichannel analog-digital
transformer and computer for reception, processing, and analysis of
the data. The amplitudes of the ordinary and extraordinary
components of the signal were averaged over every minute at all
registered altitudes. These data were used for the general estimation
of the observation results and then were averaged over time intervals
5-15 min. Using the averaged data, the electron concentration
profile
Ne(h) was calculated by the method of differential
absorption of radio waves described by
Belikovich et al. [2003a].
[5] To obtain the concentration as a function of height in the
differential absorption method
[Belrose and Burke, 1964],
the
difference in absorption along the trajectory of propagation of
ordinary and extraordinary waves is used. It is assumed that the
electron collision frequency vertical profile is known from some other
independent data. The method makes it possible to calculate the
vertical profile with a vertical shift of
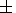 1-2 km relative to the
corresponding profile of the amplitudes of the scattered signal.
1-2 km relative to the
corresponding profile of the amplitudes of the scattered signal.
[6] Extra geophysical equipment was used at carrying out the
measurements: the installation for ionospheric drift measurements on
the basis of the space diversity reception of the scattered signal,
magnetometer, and riometer at a frequency of 32 MHz.

Powered by TeXWeb (Win32, v.2.0).
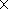 22o at the half-power level. Two circular
polarizations were received in turn and were amplified by the receiver
with the band of 40 kHz. The registration of the signal amplitudes
was performed in the height interval 50-146 km. The step of the
data reading was 1.5 km. The receiving instrumentation was
equipped by a quick-operating multichannel analog-digital
transformer and computer for reception, processing, and analysis of
the data. The amplitudes of the ordinary and extraordinary
components of the signal were averaged over every minute at all
registered altitudes. These data were used for the general estimation
of the observation results and then were averaged over time intervals
5-15 min. Using the averaged data, the electron concentration
profile
Ne(h) was calculated by the method of differential
absorption of radio waves described by
Belikovich et al. [2003a].
22o at the half-power level. Two circular
polarizations were received in turn and were amplified by the receiver
with the band of 40 kHz. The registration of the signal amplitudes
was performed in the height interval 50-146 km. The step of the
data reading was 1.5 km. The receiving instrumentation was
equipped by a quick-operating multichannel analog-digital
transformer and computer for reception, processing, and analysis of
the data. The amplitudes of the ordinary and extraordinary
components of the signal were averaged over every minute at all
registered altitudes. These data were used for the general estimation
of the observation results and then were averaged over time intervals
5-15 min. Using the averaged data, the electron concentration
profile
Ne(h) was calculated by the method of differential
absorption of radio waves described by
Belikovich et al. [2003a].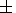 1-2 km relative to the
corresponding profile of the amplitudes of the scattered signal.
1-2 km relative to the
corresponding profile of the amplitudes of the scattered signal.