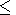
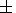 (17-25)%.
(17-25)%.
[33] The following conclusions may be drawn on the basis of the results of the atmospheric parameters measurements by the method of Bragg backscattering of radio waves at artificial periodical irregularities of the ionospheric plasma at altitudes of 95-110 km conducted in the vicinity of Nizhny Novgorod in the summer seasons of 1999-2002.
[34] The time and spatial variations in the temperature and density obtained with the help of API do not contradict to measurements by other methods [Collins et al., 1996; Jenkins et al., 1987; Kirkwood, 1986; Kurzawa and von Zahn, 1990]. They show the presence of variations with periods from 15 to 60 min corresponding to the periods of IGW observed at these heights. The vertical temperature profiles measured in the absence of atmospheric wave perturbations (IGW) demonstrate an existence of a minimum in the temperature of 120-140 K in the vicinity of 100 km.
[35] During the solar eclipse on 11 August 1999, as well as on the adjacent
days, an increased wave activity was observed. The temperature and
density variations with a period of ~1 hour were
D T/T,
D r /r 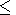
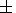 (17-25)%.
(17-25)%.
[36] In the dawn and dusk periods, there were observed IGW evidently
propagating from the terminator region. Their amplitudes were
D T/T 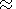 0.04-0.14 and
D r /r
0.04-0.14 and
D r /r 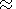 0.11-0.13 and the periods were
from 15 to 60 min.
0.11-0.13 and the periods were
from 15 to 60 min.

Citation: (2004), Measurements of the temperature and density of the upper atmosphere using artificial periodic irregularities during the summer seasons of 1999--2002, Int. J. Geomagn. Aeron., 5, GI1008, doi:10.1029/2004GI000061.
Copyright 2004 by the American Geophysical Union